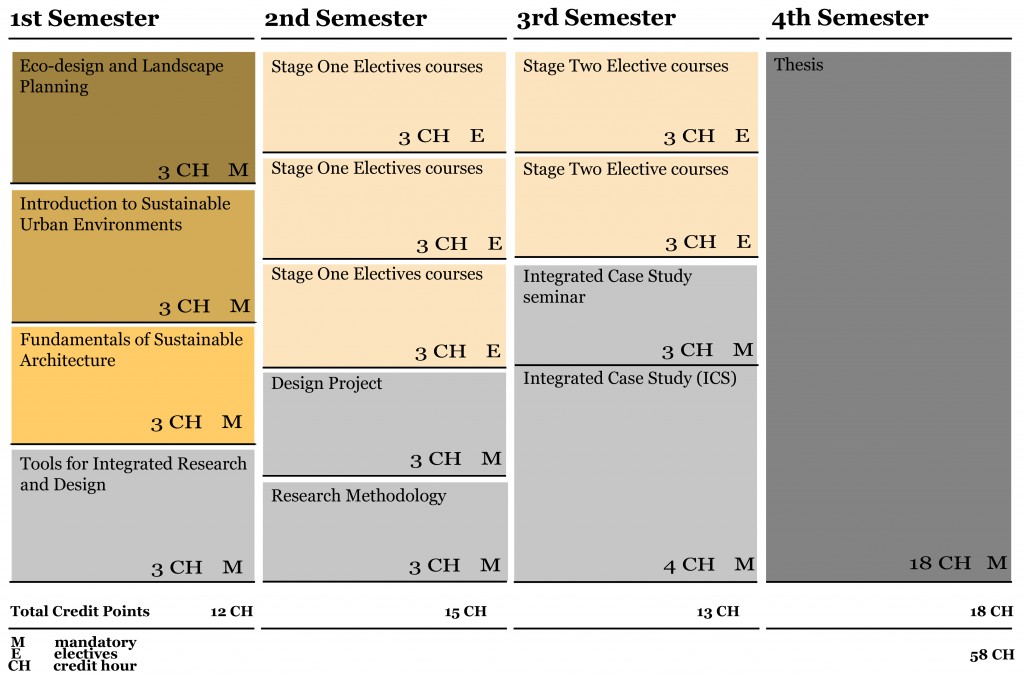
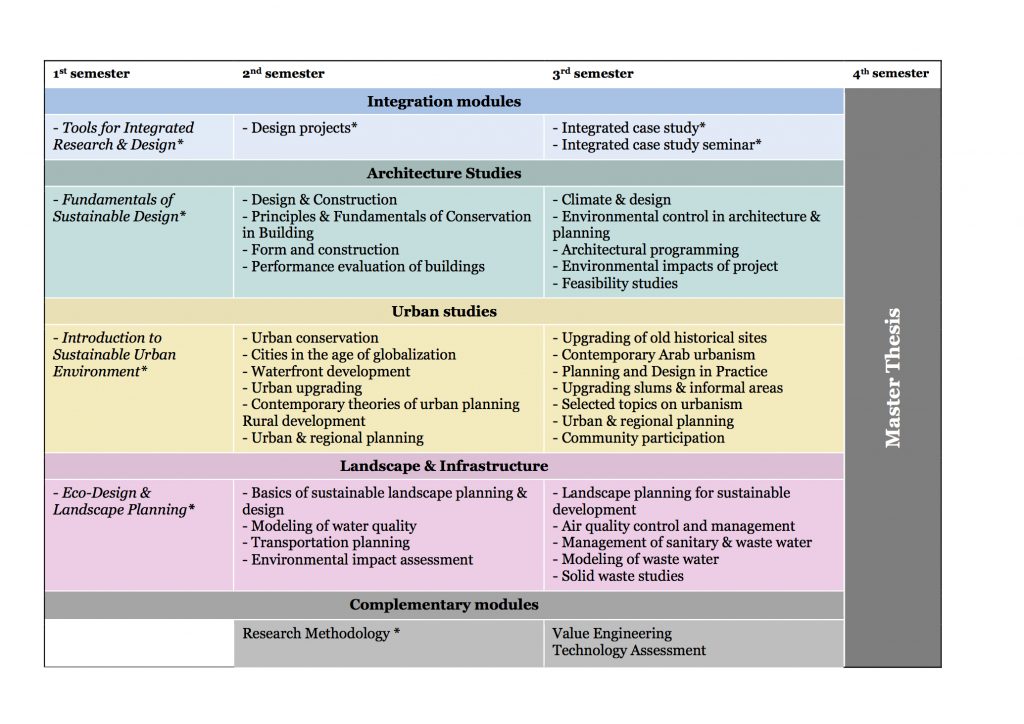
All students are required to partake in three Core Modules (first semester) and the Integrated Research and Design Modules (first to third semester). Specialization Modules and Masters Thesis topics (second to fourth semester) are chosen individually. M.Sc. IUSD operates on a studio basis.
Content of Modules
To get a first overview of the module outcomes, please consider our yearbooks:
1. Core Modules
Fundamentals of Sustainable Architecture
This course teaches basic principles of sustainable and environmentally friendly building design. Students study the principles of environmental architecture, including energy conservation, reduction of embodied energy of buildings and recycling, or the possibilities to integrate the use of solar energy and other renewable energy sources in architecture. The course also introduce the concepts of vernacular architecture, which provides “low-tech” sustainable alternatives that take into account context-specific issues such as site and local climate, regional architectural traditions and typologies, local building materials and other ecological factors, as well as socio-cultural aspects, poverty related issues and a more general recognition of the human and behavioural dimension related to programme and user.
Introduction to Sustainable Urban Environments
This module focuses on different theoretical approaches to cities, environment, social issues, urban policy-making, and to the practice of urban and regional planning in general. The course is designed to enhance the critical thinking of the students through drawing the attention to the importance of local contextual attributes when transferring theories or practices from an urban context to another. Furthermore, the course demonstrates how different theoretical approaches inform planning practices (and vice versa), as theoretical and practical approaches to planning are closely interlinked. The students are also required to analize, contextualize, and consider the introduced theoretical approaches through selected best practice examples from around the world.
Eco-design and Landscape Planning
This course aims to introduce the students to the basic principles of landscape eco-design, which are highly related to the design of green infrastructure systems. The course gives an overview on the effect of infrastructure development on landscape structure and function of urban environments, as well as the environmental challenges facing such developments. Responding to contemporary urban and infrastructure development challenges, this course brings together a series of innovative concepts and theories to discuss different methods, models and measures of ecological design of combined landscape and infrastructure systems for the 21st century.
2. Research and Design Modules
Research Methodology
This module is designed to enable graduates to prepare and write scientific research, and the preparation of reports and proposals. Graduates will be able to identify stages of scientific research such as problem identification, identifying objectives, data collection, data analysis and hypothesis testing and verification of the objectives and the like. It also aims to familiarize students with different research approaches both quantitative and qualitative, in addition to the methods of data collection and preparation of questionnaires.
Tools for Integrated Research and Design
This module offers a wide range of tools that provide students with a thorough training in general research and design skills; such as techniques for mapmaking, social, cultural and spatial analyses, statistical analyses, strategic planning tools, and visualisation as well as participatory research skills and project management skills, in addition to other methods and tools that prepare the students to work on integrated research and design projects in complex urban settings. Also, after introducing each tool and method, the students are required to utilize the introduced methods in an applied setting in relation to a given research and design project.
Design projects
This module offers students an opportunity to work with design projects that build up on each other and focus specifically on one scale and topic – they have a reduced complexity by linking design project to specific sites and stakeholder constellations. Projects will introduce the following scales: Sustainable design projects in building scale; sustainable design projects in city scale; Sustainable design projects in regional scale.
Integrated case study (core module)
In this module, students practice integrated design and planning skills and apply theoretical knowledge in a real life situation. They gain experience in data processing and analysis by developing a conceptual framework for use in an integrated design and planning process covering Regional Development Planning, Urban Planning and Design, Transportation, Ecology, and Socio-Economic Aspects. The students will work in groups with data on the study area, which will be located in the MENA Region. Topic specific planning guidelines will be developed, as well as scenario specific visions and land use plans.
Integrated case study seminar (core module)
Upon completion of these module graduates gain experience in data processing and analysis of certain topics related to their integrated case study, and gaining insights into the following topics: Regional Development Planning, Urban Planning and Design, Transportation, Ecology, and Socio-Economic Aspects.
3. Electives
The Electives cover a wide range of different disciplines in the three main IUSD research fields relating to themes of Sustainable Architecture, Sustainable Urbanism and Ecology.
Extracurricular qualifications and events
During the two academic years at MSc IUSD young professionals will have the opportunity to make use of extracurricular activities offered by the broader network and partners.
This includes:
• Workshops, and soft skills qualifications incorporated into the academic curriculum with the support by external experts.
• Workshops, and soft skills qualifications through academic networks such as DAAD (i.e. in Cairo), Webinar activities via Alumniportal Deutschland
• Webinars and Alumni workshops via sectoral network such as AGEP (German Association of Postgraduate Programmes with special Relevance to Developing Countries)
• Networking and technical exchange via GAMP (German Arab Masters Programmes Network)
• Technical and managerial qualifications (i.e. Workshops on Capacity Works) via cooperating development institutions such as GIZ
4. Masters Thesis
While most of the thesis work occurs during the last term of the second year (4th semester), students are urged to begin the process of defining a thesis topic early in the second year through their participation in a required thesis preparation seminar. The Masters thesis will ideally be developed in cooperation with external partner organizations in Egypt but it can also have a period for investigations in Germany or MENA countries. Students are required to submit a thesis on a topic of their choice that avoids the traditional perception of the thesis as a «mini-dissertation», and to think instead of a client-oriented, professional document that bridges academic and professional concerns.
For more Info, have a look at our Thesis so far.
Curriculum
All students are required to partake in three Core Modules (first semester) and the Integrated Research and Design Modules (first to third semester). Specialization Modules and Masters Thesis topics (second to fourth semester) are chosen individually. M.Sc. IUSD operates on a studio basis.
Content of Modules
To get a first overview of the module outcomes, please consider our yearbooks:
1. Core Modules
Fundamentals of Sustainable Architecture
This course teaches basic principles of sustainable and environmentally friendly building design. Students study the principles of environmental architecture, including energy conservation, reduction of embodied energy of buildings and recycling, or the possibilities to integrate the use of solar energy and other renewable energy sources in architecture. The course also introduce the concepts of vernacular architecture, which provides “low-tech” sustainable alternatives that take into account context-specific issues such as site and local climate, regional architectural traditions and typologies, local building materials and other ecological factors, as well as socio-cultural aspects, poverty related issues and a more general recognition of the human and behavioural dimension related to programme and user.
Introduction to Sustainable Urban Environments
This module focuses on different theoretical approaches to cities, environment, social issues, urban policy-making, and to the practice of urban and regional planning in general. The course is designed to enhance the critical thinking of the students through drawing the attention to the importance of local contextual attributes when transferring theories or practices from an urban context to another. Furthermore, the course demonstrates how different theoretical approaches inform planning practices (and vice versa), as theoretical and practical approaches to planning are closely interlinked. The students are also required to analize, contextualize, and consider the introduced theoretical approaches through selected best practice examples from around the world.
Eco-design and Landscape Planning
This course aims to introduce the students to the basic principles of landscape eco-design, which are highly related to the design of green infrastructure systems. The course gives an overview on the effect of infrastructure development on landscape structure and function of urban environments, as well as the environmental challenges facing such developments. Responding to contemporary urban and infrastructure development challenges, this course brings together a series of innovative concepts and theories to discuss different methods, models and measures of ecological design of combined landscape and infrastructure systems for the 21st century.
2. Research and Design Modules
Research Methodology
This module is designed to enable graduates to prepare and write scientific research, and the preparation of reports and proposals. Graduates will be able to identify stages of scientific research such as problem identification, identifying objectives, data collection, data analysis and hypothesis testing and verification of the objectives and the like. It also aims to familiarize students with different research approaches both quantitative and qualitative, in addition to the methods of data collection and preparation of questionnaires.
Tools for Integrated Research and Design
This module offers a wide range of tools that provide students with a thorough training in general research and design skills; such as techniques for mapmaking, social, cultural and spatial analyses, statistical analyses, strategic planning tools, and visualisation as well as participatory research skills and project management skills, in addition to other methods and tools that prepare the students to work on integrated research and design projects in complex urban settings. Also, after introducing each tool and method, the students are required to utilize the introduced methods in an applied setting in relation to a given research and design project.
Design projects
This module offers students an opportunity to work with design projects that build up on each other and focus specifically on one scale and topic – they have a reduced complexity by linking design project to specific sites and stakeholder constellations. Projects will introduce the following scales: Sustainable design projects in building scale; sustainable design projects in city scale; Sustainable design projects in regional scale.
Integrated case study (core module)
In this module, students practice integrated design and planning skills and apply theoretical knowledge in a real life situation. They gain experience in data processing and analysis by developing a conceptual framework for use in an integrated design and planning process covering Regional Development Planning, Urban Planning and Design, Transportation, Ecology, and Socio-Economic Aspects. The students will work in groups with data on the study area, which will be located in the MENA Region. Topic specific planning guidelines will be developed, as well as scenario specific visions and land use plans.
Integrated case study seminar (core module)
Upon completion of these module graduates gain experience in data processing and analysis of certain topics related to their integrated case study, and gaining insights into the following topics: Regional Development Planning, Urban Planning and Design, Transportation, Ecology, and Socio-Economic Aspects.
3. Electives
The Electives cover a wide range of different disciplines in the three main IUSD research fields relating to themes of Sustainable Architecture, Sustainable Urbanism and Ecology.
Extracurricular qualifications and events
During the two academic years at MSc IUSD young professionals will have the opportunity to make use of extracurricular activities offered by the broader network and partners.
This includes:
• Workshops, and soft skills qualifications incorporated into the academic curriculum with the support by external experts.
• Workshops, and soft skills qualifications through academic networks such as DAAD (i.e. in Cairo), Webinar activities via Alumniportal Deutschland
• Webinars and Alumni workshops via sectoral network such as AGEP (German Association of Postgraduate Programmes with special Relevance to Developing Countries)
• Networking and technical exchange via GAMP (German Arab Masters Programmes Network)
• Technical and managerial qualifications (i.e. Workshops on Capacity Works) via cooperating development institutions such as GIZ
4. Masters Thesis
While most of the thesis work occurs during the last term of the second year (4th semester), students are urged to begin the process of defining a thesis topic early in the second year through their participation in a required thesis preparation seminar. The Masters thesis will ideally be developed in cooperation with external partner organizations in Egypt but it can also have a period for investigations in Germany or MENA countries. Students are required to submit a thesis on a topic of their choice that avoids the traditional perception of the thesis as a «mini-dissertation», and to think instead of a client-oriented, professional document that bridges academic and professional concerns.
For more Info, have a look at our Thesis so far.